Textile Engineering & Industrial Engineering Solutions | Expert Garment, Fashion & Apparel Production Strategies - Textile Floor
Textile Fibers Useful Short Notes (Properties, Uses, Characteristics etc..) │Textile Floor│
Textile fibers can be classified into two main categories:
Natural fibers and Synthetic fibers.
Here’s a breakdown of each category..
Natural fibers and Synthetic fibers.
Here’s a breakdown of each category..
Natural Fibers
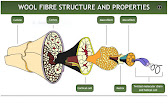
Wool fibre structure and properties │Textile Floor│
Cuticle
On the outside of the wool fibre is a protective layer of scales called cuticle cells. They overlap like tiles on a roof. The exposed edges of the cells face away from the root end so there’s more friction when you rub the fibre in one direction than the other.Polyester Fibre details, fibre properties & manufacturing process │Textile Floor│
Today over 70 to 75% of polyester is produced by
CP(
continuous polymerisation) process using PTA(purified
Terephthalic Acid) and MEG. The old process is called
Batch process using DMT( Dimethy Terephthalate) and MEG(
Mono
Ethylene Glycol).
Catalysts like 5b3O3 (ANTIMONY TRIOXIDE) are used to start
and control the reaction.Textile Cotton Fibre Details │Textile Floor│
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that
grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants
of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. Under
natural condition, the cotton balls will tend to increase the dispersion of the
seeds.
The
fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft,
breathable textile.
Textile general knowledge questions for Wet Processing Technology │Textile Floor│
Singeing: Singeing
is a process carried out to remove loose hairy fibre protruding from the surface of the cloth/yarn
by burning them.
Knitting Defects with causes & remedies │Textile Floor│
1. Drop
Stitche, 2. Pin
hole, 3. Grease
stain, 4. Fly
dust, 5. Hole
Mark, 6.
Sinker
Mark, 7. Dust
stain, 8. Needle
Mark, 9. Barre, 10. Contamination of Yarn, 11. Oil Spot, 12. Star mark, 13. Dust knit, 14. Set off, 15. Streakiness, 16. Snarls, 17. Spirality, 18. Surface
hairiness, 19. Snagging, 20. Bowing, 21. Needle
Line..
Textile general knowledge for Fabric Manufacturing Technology │Textile Floor│
1. What is knitting?
Ans. It is the process of producing fabric by transferring continuous yarns into interlocking loops, each row of loop hanging from the one immediately preceding it.
Textile general knowledge for Yarn Manufacturing Technology │Textile Floor│
Ans. Blow room....
2. What is the second process/
machine in yarn production?
Reactive Dye Properties for Textile Coloration │Textile Floor│
Knit Dyeing Process flowchart │Textile Floor│

For textile coloration of cotton fabric this process is very important to know, it will help you for to acquire knowledge all about cotton knit dyeing process. All are described below...
Subscribe to:
Posts ()